Activity Flow
The system sends and analyzes all monitored application activities in the same way, regardless of the event’s origin. Since the event collection infrastructure is agnostic to event types, the system handles an event from a Windows File Server in the same way it handles an event from Microsoft SharePoint or Microsoft Exchange.
The activity path diagram below shows a high-level process flow of events, through components, from the Activity Monitor to the Event Manager, with each blue square representing a separate component.
Activity Path
For Windows File Server, the path listed for the activity is always the physical path. This is to avoid duplication, and to avoid ambiguity of ownership and access rights.
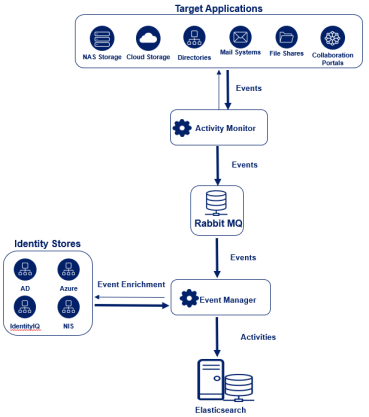
From Activity Monitor to Event Manager (Stage I to II)
| Activity | Event |
|---|---|
| Monitor | Extract the events from the monitored system using the relevant technology (to be discussed later). |
| Exclude | Raw exclusion of event is available per type of monitor. Exclusion at this level means the event will not be sent. |
| Aggregate | Similar events within the same polling interval are unified into a single event. |
| Send | Events are transformed into standard event format. The bulk is compressed, and then sent. |
| Receive | The Event Collector (inside the Event Manager) receives the events. |
From the Event Manager to the Elasticsearch and Database (Stage II to III)
| Activity | Event |
|---|---|
| Collect | Get the events from the various monitors. Verify the structure and validity, and send to a memory queue. |
| Fetch | Get the events from the memory queue and start processing. |
| Discard | Discard rules, based on event data only, are evaluated first. |
| Enrich | If required, enrich the data with identity data. |
| Evaluate | Access Rules, requiring identity data, are evaluated. Alert responses are sent. |
| Save | Save events to Elasticsearch. |
| Create BRs | For applications that do not support crawl - if the event is on a resource that is not listed - add this resource. |
Application Level Indexing (Stage IV)
After the system saves the event, Elasticsearch indexes the event data so users can construct queries on that data. By using Elasticsearch’s near real-time indexing capabilities, events are available for querying immediately after they are saved.