Configuring and Scheduling the Permissions Collection
Permissions can be analyzed to determine the application permissions of an out-of-the-box application, provided you have defined an identity store for File Access Manager to use in its analysis, and you have run a crawl for the application.
The permission collector is a software component responsible for analyzing the permissions in an application.
The Central Permission Collector Service is responsible for running the Permission Collector and Crawler tasks.
If the “File Access Manager Central Permission Collector” wasn’t installed during the installation of the server, this configuration setting will be disabled.
To configure the Permission Collection
- Open the edit screen of the required application.
- Go to Admin > Applications.
- Scroll through the list, or use the filter to find the application.
- Select the Edit icon
 on the line of the application.
on the line of the application. - Select Next until you reach the Crawler & Permissions Collection settings page. The actual entry fields vary according to the application type.
When entering this page in edit mode, you can navigate between the various configuration windows using the Next and Back buttons.
-
Central Permissions Collection Service - Select a central permission collection service from the dropdown list. You can create permissions collection services as part of the service installation process. See section "Services Configuration" in the File Access Manager Administrator Guide for further details.
-
Calculate Effective Permissions - Calculate effective permissions during the permissions collection run.
-
Calculate Riskiest Permissions - Calculates the riskiest permission on a resource – for example, Full Control is riskier than Read permissions if both are on a resource.
This option is available when selecting Calculate Effective Permissions
-
Skip Identities Sync during Permission Collection - Skip identity synchronization before running permission collection tasks when the identity collector is common to different connector.
Note
This option is checked by default.
You can now schedule a task.
Scheduling a Task
To create a schedule:
- Select Create a Schedule.
- The system will provide a Schedule Name in the format
{appName} - {type} Scheduler. Choose to keep or override this suggestion. -
Select a scheduling frequency from the dropdown list.
Schedule Frequency Options
- Run After - Create dependency of tasks. The task starts running only upon successful completion of the first task.
- Hourly - Set the start time.
- Daily - Set the start date and time.
- Weekly - Set the day(s) of the week on which to run.
- Monthly - Set the day of the month on which to run a task.
- Quarterly - Set a monthly schedule with an interval of 3 months.
- Half Yearly - Set a monthly schedule with an interval of 6 months.
- Yearly - Set a monthly schedule with an interval of 12 months.
-
Fill the Date and Time field with scheduling times. These fields differ depending upon the scheduling frequency selected.
- Select the Active checkbox to activate the schedule.
- Select Next.
Configuring and Scheduling the Crawler
-
To set or edit the Crawler configuration and scheduling
- Open the edit screen of the required application.
- Go to Admin > Applications.
- Scroll through the list, or use the filter to find the application.
- Select the Edit icon
 on the line of the application.
on the line of the application. - Select Next until you reach the Crawler & Permissions Collection settings page. The actual entry fields vary according to the application type.
-
Crawl Mailboxes, Crawl Public Folders - Select the types of folders to scan.
-
Select to open the schedule panel.
Setting the Crawl Scope
There are several options to set the crawl scope:
- Setting explicit list of resources to include and / or exclude from the scan.
- Creating a regex to define resources to exclude.
Including and Excluding Paths by List
To set the paths to include or exclude in the crawl process for an application
- Open the edit screen of the required application.
- Go to Admin > Applications.
- Scroll through the list, or use the filter to find the application.
- Select the Edit icon
 on the line of the application.
on the line of the application. - Select Next until you reach the Crawler & Permissions Collection settings page. The actual entry fields vary according to the application type.
- Scroll down to the Crawl configuration settings.
- Select Advanced Crawl Scope Configuration to open the scope configuration panel.
- Select Include / Exclude Resources to open the input fields.
- To add a resource to a list, type in the full path to include / exclude in the top field and select + to add it to the list.
- To remove a resource from a list, find the resource from the list, and select the x icon on the resource row.
When creating exclusion lists, excludes take precedence over includes.
Excluding Paths by Regex
To set filters of paths to exclude in the crawl process for an application using regex
- Open the edit screen of the required application.
- Go to Admin > Applications.
- Scroll through the list, or use the filter to find the application.
- Select the Edit icon
 on the line of the application.
on the line of the application. - Select Next until you reach the Crawler & Permissions Collection settings page. The actual entry fields vary according to the application type.
- Select Exclude Paths by Regex to open the configuration panel.
- Type in the paths to exclude by Regex, See regex examples in the section below. Since the system does not collect BRs that match this Regex, it also does not analyze them for permissions.
Crawler Regex Exclusion Example
The following are examples of crawler Regex exclusions:
Exclude all shares which start with one or more shares names:
| Example | Regex |
|---|---|
| Starting with Public Folders\shareName | Public Folders\\\\shareName$ |
| Starting with Public Folders\shareName or Public Folders\OtherShareName | Public Folders\\\\(shareName OtherShareName)$ |
Include ONLY shares which start with one or more shares names:
| Example | Regex |
|---|---|
| Starting with Public Folders\shareName | ^(?!Public Folders\\\\shareName($ \\.*)).* |
| Starting with Public Folders\shareName or Public Folders\OtherShareName | ^(?!Public Folders\\\\(shareName |
| Include ONLY one folder under a share: \server\share\folderA | ^(?!\\\\Public Folders\\shareName\$($ \\folderA$ \\folderA\\.*)).* |
Exclude all mailboxes which start with one or more user names:
| Example | Regex |
|---|---|
| Starting with John.Doe | ^Mailboxes\\John\.Doe@.* |
| Starting with John.Doe or Jane.Doe | ^Mailboxes\\(John Jane)\.Doe@.* |
Include ONLY mailboxes that start with one or more user names:
| Example | Regex |
|---|---|
| Starting with John.Doe | ^(?!Mailboxes\/John\.Doe@.*).* |
| Starting with John.Doe or Jane.Doe | ^(?!Mailboxes\/(John Jane)\.Doe@.*).* |
Note
To write a backslash or a Dollar sign, add a backslash before it as an escape character.
Note
To add a condition in a single command, use a pipe character “|” .
Narrow down the selection:
| Example | Regex |
|---|---|
| Include ONLY the C$ drive shares: \server_name*C$* | ^(?!\\\\server_name\\*C*\$($ \\.*)).* |
| Include ONLY one folder under a share: \server\share*folderA* | ^(?!\\\\server_name\\share\$($|\\ folderA $|\\ *folderA*\.)).` |
| Include ONLY all administrative shares | ^(?!\\server_name\[a-zA-Z]$($ )).* |
Note
To write a backslash or a Dollar sign, add a backslash before it as an escape character.
Note
To add a condition in a single command, use a pipe character “|” .
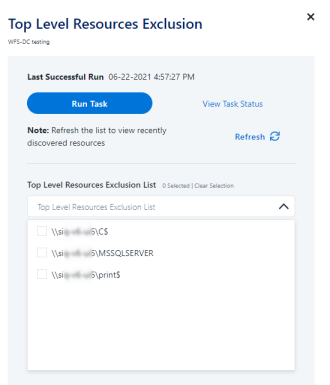
Excluding Top Level Resources
Use the top level exclusion screen to select top level roots to exclude from the crawl. This setting is done per application.
To exclude top level resources from the crawl process
- Open the application screen Admin > Applications.
- Find the application to configure and click the drop down menu on the application line. Select Exclude Top Level Resources to open the configuration panel.
-
Run Task
The Run Task button triggers a task that runs a short detection scan to detect the current top level resources.Before running the task for the first time, the message above this button is:
Note: Run task to detect the top-level resourcesIf the top level resource list has changed in the application while yo u are on this screen, press this button to retrieve the updated structure.Once triggered, you can see the task status in Settings > Task Management > Tasks.
Note
This will only work if the user has access to the task page.
When the task has completed, press Refresh to update the page with the list of top level resources.
-
Select the top level resource list, and select top level resources to exclude.
-
Select Save to save the change.
-
To refresh the list of top level resources, run the task again. Running the task will not clear the list of top level resources to exclude.
Special Consideration for Long File Paths in Crawl
If you need to support long file paths above 4,000 characters for the crawl, set the flag excludeVeryLongResourcePaths in the Permission Collection Engine App.config file to true.
By default this value will be commented out and set to false.
This key ensures, when enabled, that paths longer than 4,000 characters are excluded from the applications’ resource discovery (Crawl), to avoid issues while storing them in the SQLServer database.
When enabled, business resources with full paths longer than 4000 characters, and everything included in the hierarchical structure below them, will be excluded from the crawl, and will not be collected by File Access Manager. This scenario is extremely rare.
You should not enable exclusion of long paths, unless you experience an issue.
Background
File Access Manager uses a hashing mechanism to create a unique identifier for each business resource stored in the File Access Manager database. The hashing mechanism in SQLServer versions 2014 and earlier, is unable to process (hash) values with 4,000 or more characters.
Though resources with paths of 4000 characters or longer are extremely rare, File Access Manager is designed to handle that limitation.
Identifying the Problem
When using an SQL Server database version 2014 and ealier
The following error message in the Permission Collection Engine log file:
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException (0x80131904): String or binary data would be truncated.
In all other cases, this feature should not be enabled.
Setting the Long Resource Path Key
The Permission Collection Engine App.config file is RoleAnalyticsServiceHost.exe.config, and can be found in the folder
%SailPoint_Home%\FileAccessManager\[Permission Collection instance]\
Search for the key excludeVeryLongResourcePaths and correct it as described above.
Configuring Activity Monitoring
Configure the activity monitoring process frequency.
- Polling Interval (sec) - Activity fetching interval [in seconds]. Default is set to 60 seconds,
- Report Interval (sec) - Activity Monitor Health reporting interval [in seconds]). Default is set yo 60 seconds.
- Local Buffer Size (MB) - Local buffer size for activities [ in MB]. Default is set to 200MB.
This cyclic buffer is used to store activities on the Application Monitor’s machine in case of network errors that prevent the activities from being sent.
-
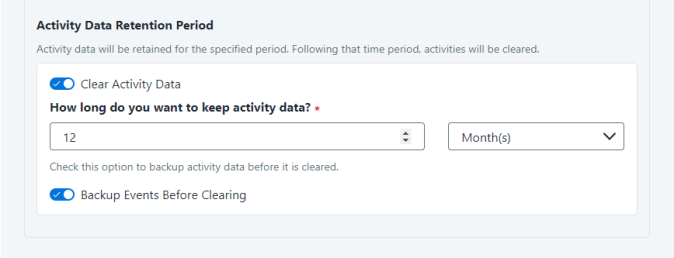
Activity Data Retention Period
Note
By default, this feature is disabled.
When selecting the Clear Activity Data option, a user is able to provide a time frame (1 to 100) in either months or years for all activity to be retained. Once that time period is met, all data will be removed.
A user can also select to backup the data before it is deleted by selecting the Backup Events Before Clearing option.
Note
The Backup Before Clearing Option will only be enabled if the backup option is set during the system installation. If a user has not selected the backup option during the installation nor provided a backup path, this option will not be enabled.
Configuring Data Enrichment Connectors
The Data Enrichment Connectors (DEC) configuration enables us to select data enrichment sources. These can be used to add information from other sources about identities.
An enrichment source could be a local HR database that is used to combine users' job descriptions or departments to the information stored in the identity store.
Select the data enrichment connectors to enrich monitored activities from the Available DECs text box.
Use the > or >> arrows to move the selected DECs to the Current DECs text box.
The user can select multiple DECs. Simply select each desired DEC.
You can create a new DEC in the Administrative Client(Applications>Configuration>ActivityMonitoring>DataEnrichmentConnectors).
After creating a new DEC, click Refresh to refresh the dropdown list.
The chapter Connectors of the File Access Manager Administrator Guide provides more information on Data Enrichment Connectors, including what they are, how to configure them, and how they fit in the Activity Flow.