Connector Overview
Accounts must be configured as described in Prerequisites for AWS, for them to be analyzed.
Capabilities
This connector enables you to use File Access Manager to access and analyze data stored in AWS S3 and do the following:
- Analyze the structure of your stored data.
- Monitor user activity in the resources.
- Classify the data being stored.
- Verify user permissions on the resources, and compare them against requirements.
- Manage access fulfillment - automated granting and revoking of access - according to rules set in File Access Manager.
- Identity collector – collect IAM users, groups and roles and the connections between them.
See the File Access Manager documentation for a full description.
Crawler
The crawler analyzes the structure of the organization and builds the hierarchy tree
- Organization Root container
- Organization Units (OUs)
- AWS Accounts
- S3 Buckets
- S3 Folders
Analyze all Objects in S3 Buckets
- If Analyze all Objects is checked, the crawler will get also the S3 Objects (files) under the buckets, their size and total size of the containing folder.
Permission Collector
The Permission collection will retrieve and analyze the following permissions:
- ACLs of buckets. If Analyze ACLs is checked, ACLs will be collected for the objects retrieved in the crawl.
- Bucket policies for the buckets and their objects.
- IAM policies which are relevant for the S3 buckets and Objects.
- Account and bucket level PublicAccessBlock configurations.
- Cross account permissions.
Permission collection limitations and unsupported features:
- Permissions are analyzed for buckets and objects, not for folders since they are not an actual object in S3.
- Permissions Boundary.
- Policies Conditions.
- Policies Variables.
- Policies elements - NotPrincipal, NotAction, NotResource.
- Only S3 related permissions are analyzed.
- Access points and Jobs permissions are not analyzed.
Identity Collection
The AWS identities will be collected by the permission collector at the beginning of the task.
- The following identities are collected:
- AWS Accounts (root users)
- IAM Users
- IAM Groups
- IAM Roles
- The AWS predefine groups are represented as the following groups:
http://acs.amazonaws.com/groups/global/AllUsers
“Anonymous” with type "Everyone or Authenticated Users, or contains it".http://acs.amazonaws.com/groups/global/AuthenticatedUsers
“AwsAuthenticatedUsers” with type "Everyone or Authenticated Users, or contains it".http://acs.amazonaws.com/groups/s3/LogDelivery
“S3LogDelivery” with type “Local Group”. - From each IAM Role, File Access Manager collects its trusted entities as members of the role.
- The AWS entities will be mapped to the following types:
- IAM Users – will be saved as FAM “Local User” type.
- IAM Groups – will be saved as FAM “Local Group” type.
- IAM Roles – will be saved as FAM “Local Role” type.
- AWS Account – will be saved as FAM “AWS Account” type.
- AWS Service – will be saved as FAM “AWS Service” type.
- All other types, including “Federated”, etc. , – will be saved as FAM “AWS External Account” type.
- IAM Role trusted Identity of type "*" is represented as “Anonymous” with type "Everyone, Authenticated Users, or contains it".
- "Principal": "*" in bucket policy is represented as “Anonymous” with type "Everyone, Authenticated Users, or contains it".
- For each Collected identity, the primary ID will be their Arn and Alternative Ids will be collected as well:
- For AWS Accounts – Id, root user Arn
arn:aws:iam::{iamRootUser.Id}:rootand canonical Id. - For other identities – Id.
- For AWS Accounts – Id, root user Arn
- Additional information that is collected:
- Name
- Display Name
- Description
- Domain – will be the AccountName(#AccountId)
- Email (Only for Aws Account)
- LastLogin (Only for IAM Users)
Cross Account Access
To achieve cross account access, and allow an AWS IAM Identitiy from Account A to access AWS resources in account B (S3 resource in our case) two conditions must be met:
-
The IAM Identity owner account A should give permission X on the S3 resource in account B.
- In File Access Manager this permission will appear as X-ByTrustedCrossAccount.
-
The S3 resource owner account B should give permission X on the resource to the IAM Identity from account A.
- In File Access Manager this permission will appear as X-ByTrustingCrossAccount.
Permission X will be affective only if both permissions are granted to the user / group on the resource. Otherwise, the user / group will not be allowed to perform X on this resource.
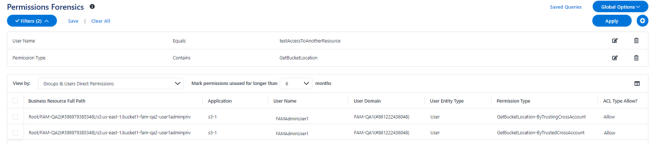
In the example above, the user “FAMAdminUser1” from account “FA-QA1” has both “GetBucketLocation-ByTrustingCrossAccount” and “GetBucketLocation-ByTrustedCrossAccount” permission on bucket “bucket1-fam-qa2-user1adminpriv” from account “FAM-QA2”.
Cross Account by Assume Roles
This scenario requires 4 conditions for user USER_A from account A to have permission X on resource RESOURCE_B from account B through role ASSUME_ROLE_B:
- ASSUME_ROLE_B is defined in account B.
- ASSUME_ROLE_B is attached to policy that gives permission X on RESOURCE_B.
- USER_A should be a member of ASSUME_ROLE - a trusted entity of the role.
-
USER_A should have in account A, permission to assume ASSUME_ROLE_B in account B.
Note
File Access Manager does not display this information in v8.2.
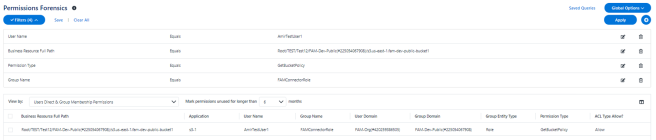
In the example above, the role “FAMConnectorRole” allows “GetBucketPolicy” on bucket “fam-dev-public-bucket1”. The role and the bucket, both belong to account “FAM-Dev-Public”. The role has a member user (trusted entity) “AmirTestUser1” from account “Fam-Org”.
If in account FAM-Org, “AmirTestUser1” has a policy which allows it to assume the role “FAMConnectorRole” in account “FAM-Dev-Public” (Not supported in File Access Manager view in v8.2) – The permission will be active.
Block Public Access
The Amazon S3 Block Public Access feature provides settings for buckets and accounts to help manage public access to Amazon S3 resources. By default, new buckets and objects don't allow public access. However, users can modify bucket policies or object permissions to allow public access. S3 Block Public Access settings override these policies and permissions and enable to limit public access to these resources.
There are 4 settings both on the bucket level, and the account level. If the PublicAccessBlock settings are different between the bucket and the account, Amazon S3 uses the most restrictive combination of the bucket-level and account-level settings.
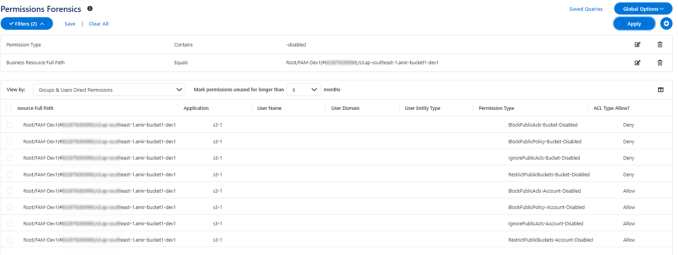
In File Access Manager these permissions appear with the suffix “Account-Disabled” for the account level settings and “Bucket-Disabled” for the bucket level settings. If one of these settings is turned off, the Permission Forensics view shows these permissions as “Allow”.
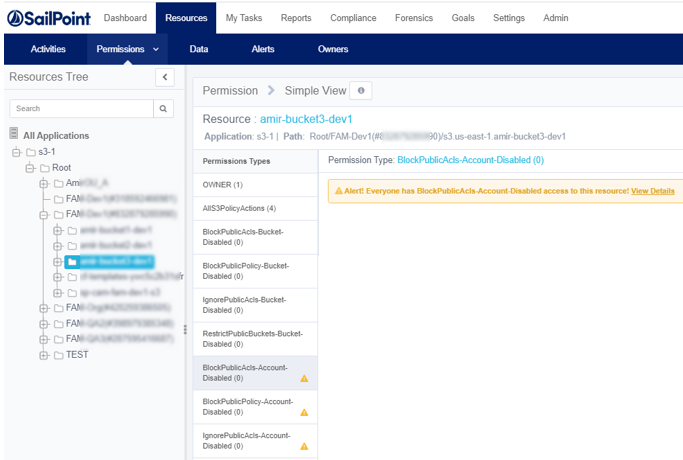
In the admin client, in Resources > Permissions > Simple View they will appear with warnings.
AWS S3 Installation Flow Overview
To install the AWS S3 connector:
- Configure all the prerequisites.
- Add a new AWS S3 application in the Business Website.
- Install the relevant services:
- Activity Monitor - This is the activity collection engine, used by all connectors that support activity monitoring.
- Permissions CollectorIf you are using EC2 login, the collector should be installed on the EC2 instance.
- Data Classification Collector.
Important
Installing the permissions collector and data classification services is optional and should only be installed by someone with a full understanding of File Access Manager deployment architecture. The File Access Manager Administrator Guide has additional information on the architecture.