Permission Forensics
Permission Forensics allows the administrator to monitor and analyze the user and group permissions. On this screen you can create queries to analyze the permissions of specific groups of users, save and share queries for selecting users and groups, generate reports, run permission scans, and revoke explicit permissions of users.
This page supports reports and campaigns.
This component answers questions, such as:
- Which users have access to what resources?
- Which users have not used permissions granted to them?
- Which permissions were granted to each group?
- Which groups are not being used?
The table displays the permissions according to the level of granularity selected in the filter.
When creating a filter, you can define the granularity of the report using the View by field, and can mark stale permissions on the table according to the unused time selected.
Note
The query retrieves the first 100,000 results. Narrow the search to obtain a better fit.
Reports - See Generating Forensics Reports.
Filters - See Filters: Creating and Editing a Forensics Query
Viewing Permission Forensics
The Permission Forensics table displays the permissions retrieved by the query run. By default, the data displayed includes the following columns for each permission:
Resource
- Business resource full path
- Application
User
- User name
- User display name
- Group name
- User domain
- Group domain
- User entity type
- Group entity type
Permission
- Permission type
- Classification category
- Is inherited
- Inherits permissions
- ACL type allowed?
To change the order of the columns, drag the column titles.
Additional columns available: - Application group, Application type, Business Resource Logical Path, Business Resource Name, Business Resource Type, Creates Loop, Creation Timestamp, Cumulative Last Used, Department, Distinguished Name, Group Path, Is Effective, Is Owner Permission, Is Riskiest, Is, SID History, Last Login Date, Last Used Date, Loop Path, Password Never Expires, Password Not Required, Permission Type Description, User Disabled, User Email, User Locked
To select columns to display:
- Select the column chooser icon on the table header bar.
- Select the columns to display from the dropdown list.
- Click Show All / Show Less to display a full list of columns / only the default columns in the column chooser. This does not change the selection of columns to display in the table.
- Use the search field to narrow down the list of columns in the column chooser.
- Click Reset Columns to reset to the default selection and order of the columns in the table.
View By
The default view is the Users and Groups view.
You can change the granularity of the output by selecting the View By type. These options determine whether to check a user’s direct permissions or permissions granted by groups the user belongs to, as described below:
- Groups & Users direct Permissions – this view displays direct Users’ and Groups’ permissions but does not display the Group members.
- Users direct & Group membership Permissions – this view displays user permissions based on direct permission, group membership, and nested group membership. This view doesn't list the users in the groups Everyone and Authenticated Users.
- Everyone Groups expanded, Users direct & Group membership Permissions – this view displays user permissions based on direct permission, group membership, and nested group membership, including listing the members of the Everyone and Authenticated Users groups.
Note
In the Permission Forensic screen, the View By field can be changed after setting or restoring the filter.
Scope and Hierarchical Search
By default, when you select a Business Resource to scope its permissions, only the direct Business Resource permissions (not the child BR permissions) display.
Special Groups - Group Entity Type
When creating a filter, you can select the group entity type from Field.
In Windows-based environments, the user groups are Everyone, Authenticated Users, and Domain Users.
Everyone - Includes all users.
Authenticated Users - Includes all internal users.
Domain Users - Includes a group with all users in the domain. By default, any user created is a member of this group, though it is possible to remove that user.
Owner Permission Field
Data Access Security permission forensics allows identification and tracking of Owner permissions in the following ways:
- A proprietary column titles “Is Owner Permission” indicates whether a given permission is an Owner permission.
- A proprietary query attribute is dedicated for filtering Owner permissions allowing queries and/or reports listing the owners of resources.
Permission Scan for Business Resource
The permission scan collects the security information from the scanned Business Resources and stores it in the Data Access Security database. This includes which users or groups have access to the Business Resource and whether the access is inherited. The permission scan stores access types such as read, write, full control, etc., depending on the application type.
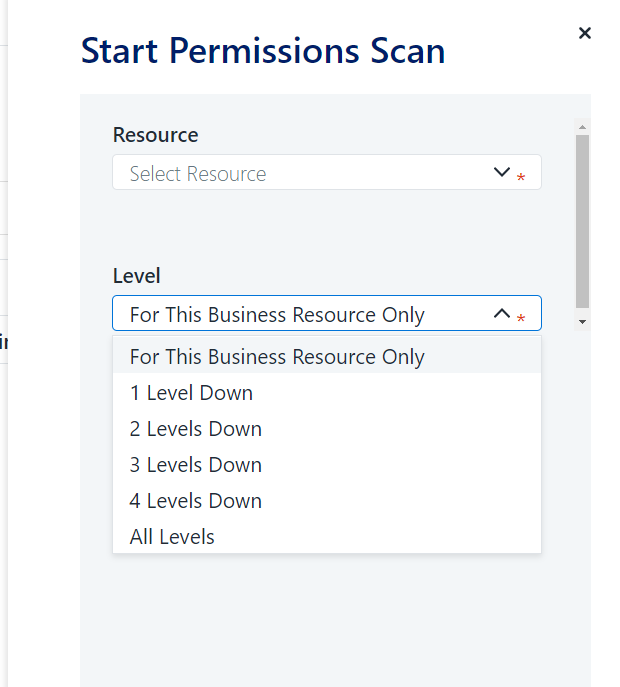
When requesting a permission scan, you can set the resources to scan and the number of levels below the requested Business Resource.
Performing a Permission Scan
- Navigate to Forensics > Permissions.
-
From the Global Options dropdown menu, select Start Permission Scan.
This opens the Permission Scan panel.
-
Select the scan level:
- This Business Resource only
- This Business Resource and levels 'Level 1-4' and 'All Levels'
-
Click Scan to start the scan or Cancel to return to the Permission Forensics screen.
DFS Support
For DFS resources, the Permission Forensics table will show the physical and the logical path of resources.
You can create a filter for DFS resources by logical path only. To select a logical path, select Resource on the Select Field drop down menu. Next, navigate to the required path on the resource tree by using the Select Resource dropdown menu. (See Searching for Resources Using a Resource Tree).
Documentation Feedback
Feedback is provided as an informational resource only and does not form part of SailPoint’s official product documentation. SailPoint does not warrant or make any guarantees about the feedback (including without limitation as to its accuracy, relevance, or reliability). All feedback is subject to the terms set forth at https://developer.sailpoint.com/discuss/tos.