Terminology: Users and User Permissions
The terms used in the File Access Manager website and File Access Manager Administrative Client refer to users and user permissions in two different contexts:
-
Business Resource Users
Entities within the organization, their access permissions to various company resources, and the activities they perform on these resources.
Users
Entities such as company employees and bots with access to company resources.
User permissions
Permissions or capabilities granted to a user to perform tasks such as reading and writing to a windows file server, sending emails, writing to Google Drive, deleting files, etc.
-
File Access Manager Website Users
Administrators and users of File Access Manager and their access permissions to various parts of the application. What reports they can run, what resources they are allowed to view, etc.
The following terms are used to define the users and access permissions in these contexts:
|
Context
Term |
Business Resource Users (#1 above) |
File Access Manager Website Users (#2 above) |
File Access Manager Administrative Client users |
|
User |
“User” |
“User” |
“User” |
|
Groups of users |
“Group”
|
“Group Account” |
|
|
Permission |
“Permission”
|
“Right”
|
“Permission”
|
|
Group of permissions |
|
“Capability”
|
“Role”
|
|
Resources user is allowed to access |
Part of “Permissions” |
“User Scope” (* The user can access these resources in the context of File Access Manager, and not the resources themselves) |
“User Data Role” |
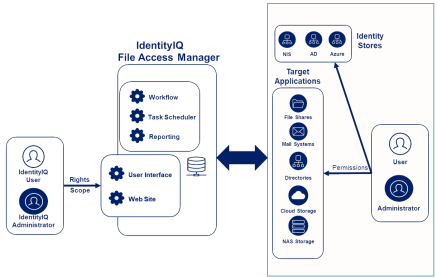
Permissions define which users can access which files on a given application resource, such as permission to a given directory or message group.
Rights define what which sections, screens, etc. users can access and what actions they can do there.
Scope may refine rights further based on an entity's role within the organization or tasks they need to complete.