Interceptors in a Shared RACF Database Environment
A shared RACF database environment consists of two or more RACF systems which share the same RACF database.
In a shared database configuration, one of the systems runs a full instance of Connector for RACF. This system is referred to as the primary system. Each additional RACF system sharing the database is referred to as a secondary system. Each secondary system only runs one component of Connector for RACF the Interceptor.
The primary system communicates with IdentityIQ and executes the transactions generated by IdentityIQ (in the regular manner). The secondary systems runs the Connector Interceptors to ensure that any updates made to the RACF database from these systems are propagated to IdentityIQ. In this way, the IdentityIQ and RACF databases are kept synchronized.
For example, assume that systems SYSA and SYSB share the RACF database. SYSA is the primary system and runs the complete Connector for RACF. SYSB is the secondary system which runs only the Online Interceptor. This configuration is shown in the following flowchart.
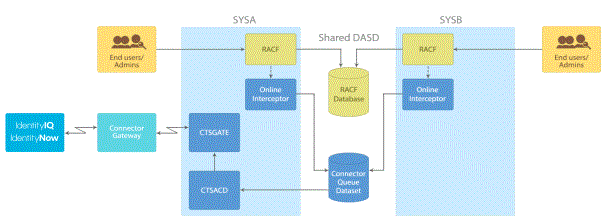
When a transaction is issued by IdentityIQ, it is executed by the Connector Transaction Server (CS) running on the primary system, and the appropriate updates are made to the RACF database.
When a local update is done in either SYSA or SYSB, it is intercepted by the appropriate Interceptor running in the system and written to the Connector QUEUE dataset.
The Notification Server (CD) running in the primary system reads the local update from the Connector QUEUE dataset and forwards it to Connector for RACF Gateway which passes it to IdentityIQ. This ensures that the IdentityIQ and RACF databases are kept synchronized.