Integrating SailPoint with SAP GRC
Revised Date: 19 January 2026
Note
This is an integration and requires additional licensing or subscriptions to utilize it. For more information, contact your customer success manager.
Note
IdentityIQ connector information is now available as online help and PDF. The online help also describes the latest updates for the connector.
To find documents related to a specific version of IdentityIQ, refer to the Supported Connectors for IdentityIQ page on Compass.
Configuration details for connectors may vary not only by release version but also by patch version. Be sure to refer to the correct documentation for your specific release and patch level.
This document is designed to provide the information required to configure a working instance of a SAP GRC connector for SailPoint. This connector supports:
This integration is used to leverage SAP GRC's ability to perform SOD (Separation of Duties) checks and take remediation or mitigation decisions within the SAP GRC. The mitigation decision must be taken in SAP GRC so that SAP GRC is aware of the mitigation controls, which are applied on risks, and would not report these risks until the time mitigation is applicable.
The SAP GRC connector enables checking for risk in the request placed in IdentityIQ (containing SAP Direct Roles and Profiles) using the following method:
-
Request is sent to SAP GRC for proactive check.
-
ARA Web Service checks for risk present in the request, if no risk is returned then IdentityIQ continues provisioning the request.
-
If ARA Web Service returns a risk in the request, then a corresponding request is created in SAP GRC using the ARM Web Service.
-
IdentityIQ continues polling the request until a response issued by SAP GRC.
-
On the basis of the response returned in the previous step (approval or rejection by SAP GRC), IdentityIQ continues with provisioning or rejects the request.
This integration is used to aggregate all the Users and Roles from the systems (SAP SCM, JAVA, SAP ERP HCM, and so on) connected to SAP GRC and facilitates their provisioning by creating requests in GRC irrespective if there is risk present or not, as illustrated in the following figure:
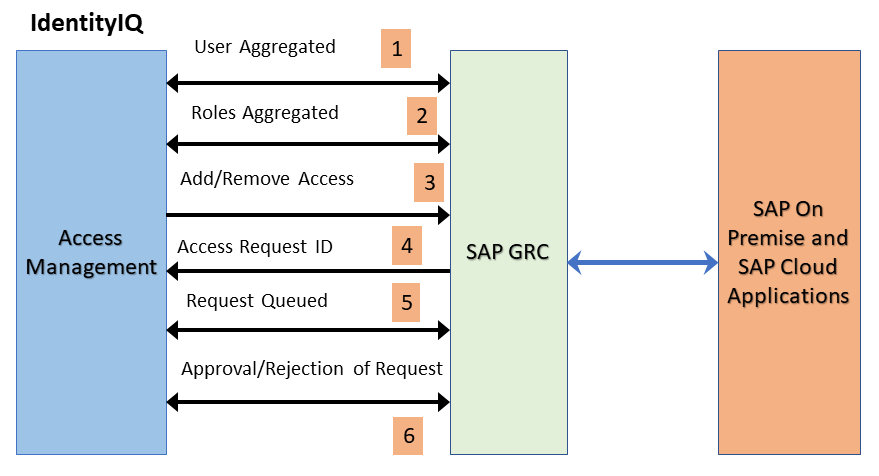
The figure explains the following methods:
-
User Aggregated from the GRC connected system.
-
Roles Aggregated from the GRC connected system.
-
Request sent for adding or removing access to the connected system.
-
Access Request ID created in GRC.
-
Requests wait and are queued until a response is issued by SAP GRC.
-
On the basis of the response returned from SAP GRC (approval or rejection in GRC ), SAP GRC provisions or rejects the request and the corresponding status is maintained in the SAP GRC source.
The Risk Management Integration performs risk analysis which helps to find whether the requested access has violations on IdentityIQ. When a Risk Management mode is selected, only the Access Risk Analysis (ARA) module is required as compared to the Risk Analysis mode, where both the Access Risk Analysis(ARA) and the Access Request Management (ARM) modules were required. In the Access Risk Analysis and Access Request Management modules integration, when the end user requests access from IdentityIQ the request goes though IdentityIQ approvals. Once it is approved on the IdentityIQ side, it goes to SAP GRC for a risk analysis check. If a violation is shown, the integration creates a request in the SAP GRC ARM for further processing. If no risk is found, the request goes ahead for provisioning the access. In the Risk Management Integration, whenever a new access request is raised it goes to the SAP GRC ARA module for risk analysis. If the requested access has any violations, a policy violation message is raised on IdentityIQ before creating the access request ticket in IdentityIQ . The requester will receive an option to remove risky entitlements, and the approver can also view the violations before approving or denying the access.
Note
SAP GRC IAG Bridge is an additional optional feature provided in the existing SailPoint SAP GRC connector. An existing SailPoint SAP GRC connector set up is a prerequisite for this feature.
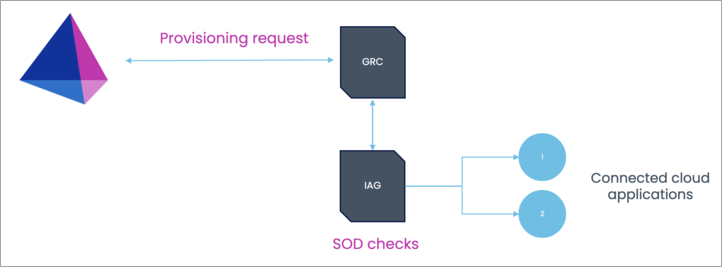
SAP GRC IAG Bridge is an additional setup on top of an existing SAP Access Control (GRC) on-premise solution, which communicates with SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance (IAG). This feature extends access governance functionality to cloud systems in a hybrid landscape.
IAG Bridge is a SAP suggested approach for the customers who have invested heavily in SAP GRC access control, but now want to provide support for cloud applications as well. This configuration helps to perform risk analysis of user requests in IAG for connected SAP cloud systems using the SAP GRC system as a bridge.
The major benefit for this integration is that the source of truth for access requests and risk analysis remains to be SAP GRC, and IAG acts as secondary system to communicate with cloud applications. Separate licenses must be procured from SAP for both GRC and IAG systems to use this feature.
Warning
The RFC_READ_TABLE integration function module is deprecated as of January 2023. All enhancements and fixes after this date are only supported on the SailPoint ABAP Function Module. For more information, refer to the announcement post. For more information on configuration, refer to SailPoint Add-On to replace the use of RFC_READ_TABLE.
-
Enhanced to exclude certain systems linked to GRC from user aggregation, provisioning, and attribute update operations.
-
Enhanced to support the provisioning and de-provisioning of Fire Fighter IDs (FFID), as user entitlements in SAP GRC.
-
Supports SAP GRC Access Control 12.0 SP26.